Portal:Astronomy
|
The Astronomy Portal
Introduction Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxies, meteoroids, asteroids, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Egyptians, Babylonians, Greeks, Indians, Chinese, Maya, and many ancient indigenous peoples of the Americas. In the past, astronomy included disciplines as diverse as astrometry, celestial navigation, observational astronomy, and the making of calendars. Professional astronomy is split into observational and theoretical branches. Observational astronomy is focused on acquiring data from observations of astronomical objects. This data is then analyzed using basic principles of physics. Theoretical astronomy is oriented toward the development of computer or analytical models to describe astronomical objects and phenomena. These two fields complement each other. Theoretical astronomy seeks to explain observational results and observations are used to confirm theoretical results. Astronomy is one of the few sciences in which amateurs play an active role. This is especially true for the discovery and observation of transient events. Amateur astronomers have helped with many important discoveries, such as finding new comets. (Full article...) General images -The following are images from various astronomy-related articles on Wikipedia.
This is a Featured article, which represents some of the best content on English Wikipedia.
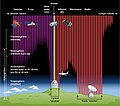
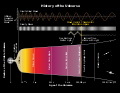
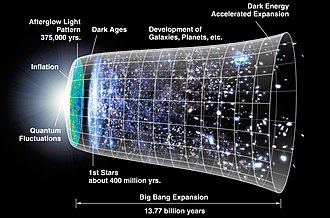 The Big Bang is a physical theory that describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature. It was first proposed in 1927 by Roman Catholic priest and physicist Georges Lemaître. Various cosmological models of the Big Bang explain the evolution of the observable universe from the earliest known periods through its subsequent large-scale form. These models offer a comprehensive explanation for a broad range of observed phenomena, including the abundance of light elements, the cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation, and large-scale structure. The overall uniformity of the universe, known as the flatness problem, is explained through cosmic inflation: a sudden and very rapid expansion of space during the earliest moments. However, physics currently lacks a widely accepted theory of quantum gravity that can successfully model the earliest conditions of the Big Bang. Crucially, these models are compatible with the Hubble–Lemaître law—the observation that the farther away a galaxy is, the faster it is moving away from Earth. Extrapolating this cosmic expansion backwards in time using the known laws of physics, the models describe an increasingly concentrated cosmos preceded by a singularity in which space and time lose meaning (typically named "the Big Bang singularity"). In 1964 the CMB was discovered, which convinced many cosmologists that the competing steady-state model of cosmic evolution was falsified, since the Big Bang models predict a uniform background radiation caused by high temperatures and densities in the distant past. A wide range of empirical evidence strongly favors the Big Bang event, which is now essentially universally accepted. Detailed measurements of the expansion rate of the universe place the Big Bang singularity at an estimated 13.787±0.020 billion years ago, which is considered the age of the universe. (Full article...)Did you know -
More Did you know (auto generated)
WikiProjectsSelected image - An Einstein ring is created when light from a galaxy or star passes by a massive object en route to the Earth. "Smiley" image of galaxy cluster (SDSS J1038+4849) & gravitational lensing (an Einstein ring) (HST). Astronomy News
April anniversaries
Astronomical eventsAll times UT unless otherwise specified.
TopicsSubcategoriesSelect [►] to view subcategories
Things you can do
WikibooksThese books may be in various stages of development. See also the related Science and Mathematics bookshelves.
WikijuniorAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Discover Wikipedia using portals Shortcuts to this page: Astronomy portal • P:ASTRO Purge server cache |