Sechium
| Sechium | |
|---|---|
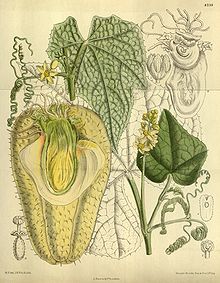
| |
| Sechium edule | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Cucurbitales |
| Family: | Cucurbitaceae |
| Subfamily: | Cucurbitoideae |
| Tribe: | Sicyoeae |
| Genus: | Sechium P.Browne |
| Synonyms[1] | |
Sechium was a genus of plants now subsumed into the genus Sicyos:[2] also placed in the tribe Sicyoeae of the gourd family, Cucurbitaceae. Its best known member was the edible and widely cultivated chayote.
Species[edit]
Previously accepted species in the genus were:[3]
- Sechium chinantlense Lira & F. Chiang
- Sechium compositum (Donn. Sm.) C. Jeffrey
- Sechium edule (Jacq.) Sw. The chayote or christophene
- Sechium hintonii (Paul G. Wilson) C. Jeffrey
- Sechium mexicanum Lira & M. Nee
- Sechium panamense (Wunderlin) Lira & F.Chiang
- Sechium pittieri (Cogn.) C.Jeffrey
- Sechium tacaco (Pittier) C. Jeffrey
- Sechium talamancensis (Wunderlin) C.Jeffrey
- Sechium venosum (L.D.Gómez) Lira & F.Chiang [4]
- Sechium villosum (Wunderlin) C. Jeffrey

References[edit]
- ^ "USDA GRIN Taxonomy".
- ^ POWO: retrieved 11 March 2024
- ^ The Plant List (2013). Version 1.1. Published on the Internet; http://www.theplantlist.org/ (accessed 11 March 2016)
- ^ Rafael Lira Saade (1996). Chayote: Sechium edule (Jacq.) Sw (PDF). International Plant Genetic Resources Institute.
